At its core, an SSO portal is an authentication service that enables users to access multiple applications by logging in just once. Instead of having separate login credentials for each application, the SSO portal acts as a gateway, providing a unified login experience. This eliminates the need for users to remember multiple usernames and passwords, reducing the likelihood of password fatigue—a common issue where users struggle to keep track of numerous login details.
SSO portals are commonly used in corporate environments, educational institutions, and other organizations where users need access to a range of applications, such as email services, file storage systems, HR portals, and more. By streamlining the login process, SSO portals enhance both security and convenience, making them an essential tool in today’s digital landscape.
How Does an SSO Portal Work?
An SSO portal operates on the principle of federated identity management, which involves linking a user’s identity across multiple systems. When a user logs in to the SSO portal, the portal authenticates the user’s credentials against a central identity provider (IdP). Once authenticated, the user is granted access to all connected applications without needing to log in again.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how an SSO portal typically works:
-
User Authentication: The user accesses the SSO portal and enters their login credentials (username and password). The portal then sends these credentials to the identity provider for verification.
-
Token Generation: Upon successful authentication, the identity provider generates an authentication token or assertion. This token is a piece of encrypted data that verifies the user's identity and is used for subsequent logins.
-
Token Exchange: The SSO portal exchanges the authentication token with the service providers (applications) that the user needs to access. Each service provider verifies the token with the identity provider to ensure it is valid.
-
Access Granted: Once the token is verified, the user is granted access to the requested application without needing to re-enter their credentials. The same token can be used to access other connected applications as well.
This entire process happens seamlessly and within seconds, providing users with a smooth and hassle-free login experience.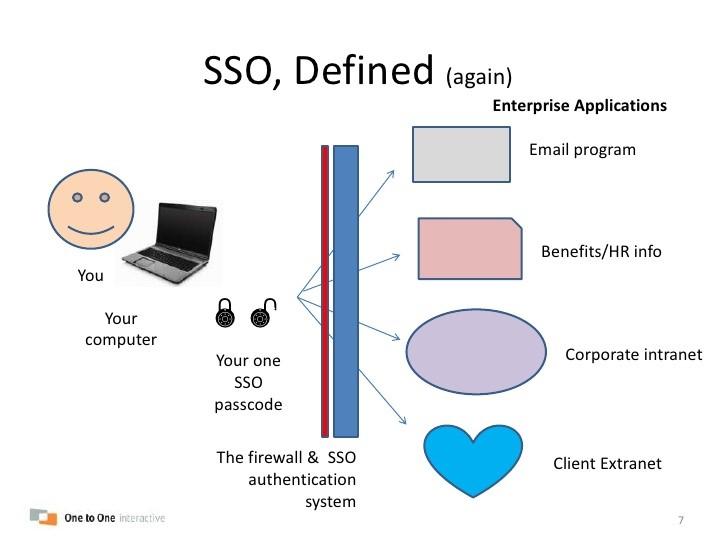
Benefits of Using an SSO Portal
The implementation of an SSO portal offers numerous benefits for both users and organizations:
-
Enhanced User Experience: The most significant advantage of an SSO portal is the improved user experience. Users no longer need to juggle multiple passwords or face the frustration of resetting forgotten passwords. A single login provides access to all necessary applications, making the user experience more efficient and enjoyable.
-
Increased Security: SSO portals reduce the risk of weak password practices, such as reusing passwords across different applications. Since users only need to remember one password, they are more likely to create a strong, unique password. Additionally, SSO portals can be integrated with multi-factor authentication (MFA) for an added layer of security, further protecting user accounts from unauthorized access.
-
Simplified IT Management: From an administrative perspective, SSO portals simplify the management of user accounts. IT departments can easily manage user access rights and permissions from a central location, reducing the complexity of account provisioning and deprovisioning. This centralized control also makes it easier to enforce security policies across all connected applications.
-
Cost Efficiency: By reducing the number of help desk calls related to password resets, organizations can save on support costs. Additionally, SSO portals reduce the time employees spend logging in and out of different systems, increasing productivity and overall operational efficiency.
-
Compliance and Auditing: SSO portals provide organizations with better control over user access, which is crucial for compliance with regulatory requirements. Centralized logging and auditing capabilities make it easier to track user activity across multiple applications, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
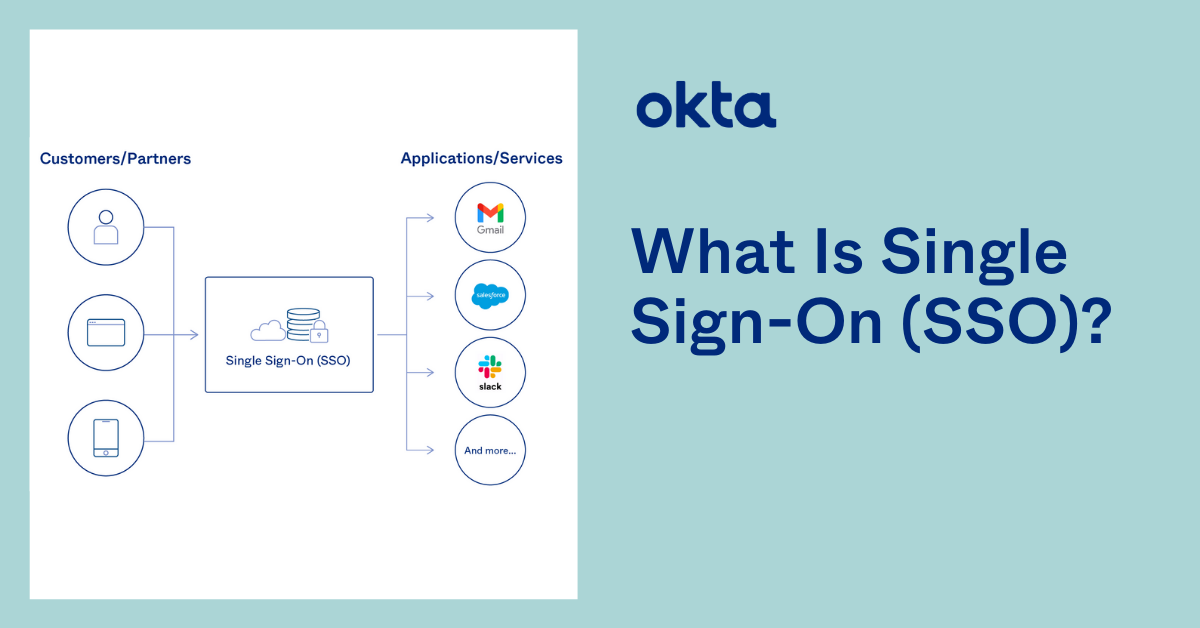
Common Use Cases for SSO Portals
SSO portals are widely used across various industries and sectors, including:
-
Corporate Environments: Employees in large organizations often need to access numerous internal and external applications daily. SSO portals streamline this process, enabling employees to focus on their work rather than managing multiple logins.
-
Educational Institutions: Students, faculty, and staff require access to a range of online resources, such as learning management systems, email platforms, and research databases. SSO portals make it easier to manage these access points, enhancing the overall educational experience.
-
Healthcare: Healthcare providers often use SSO portals to manage access to electronic health records (EHRs), scheduling systems, and other critical applications. This ensures that healthcare professionals can quickly and securely access patient information when needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an SSO portal is a powerful tool that enhances both security and convenience in the digital world. By providing a centralized authentication service, SSO portals simplify the user experience, reduce the risk of password-related security breaches, and streamline IT management. As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, the adoption of SSO portals is likely to grow, making them an indispensable component of modern digital infrastructure.



