In the world of precision manufacturing, achieving high levels of accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency is essential to producing quality products. To meet these requirements, manufacturers rely on specialized tools such as jigs and fixtures. These tools help hold, support, and position workpieces accurately during machining, welding, and assembly operations.
While jigs and fixtures may sound similar, they serve distinct roles and each is tailored to specific manufacturing processes. In this article, we will dive into the differences between jigs and fixtures, explore the types of both tools, and understand how they benefit manufacturers in various industries.
What Are Jigs and Fixtures?
Both jigs and fixtures are mechanical devices used in the manufacturing process to ensure precision and consistency. They are designed to hold, position, or guide workpieces during machining operations, resulting in high-quality and repeatable parts. However, the primary difference between them lies in their function:
-
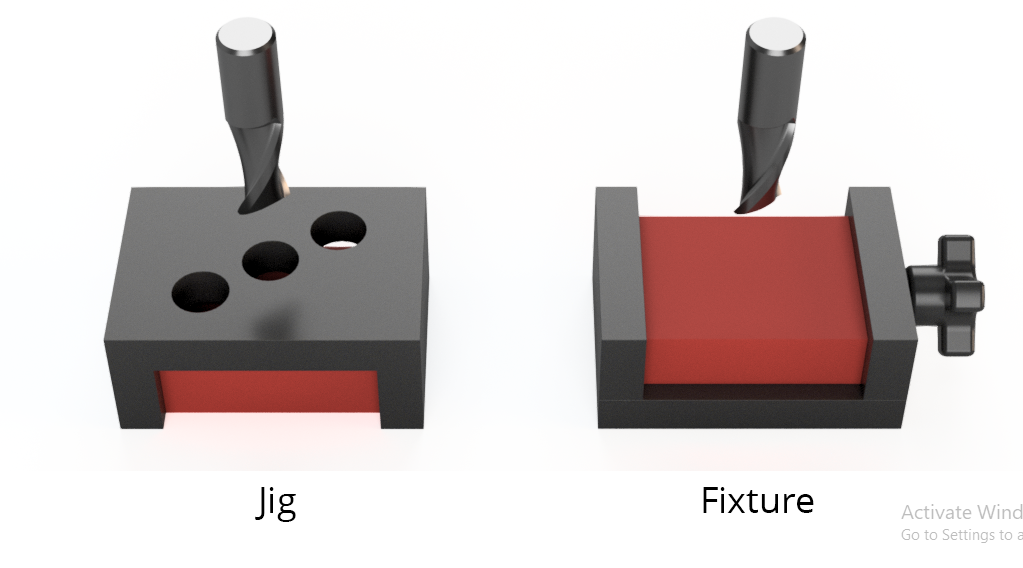
Jigs: A jig is a tool that holds the workpiece in place while also guiding the cutting tool during machining. Jigs are primarily used in operations where a cutting tool (like a drill, mill, or tap) must follow a specific path to ensure precision and consistency.
-
Fixtures: A fixture, by contrast, is a device used to hold the workpiece securely during machining, but it does not guide the cutting tool. Fixtures simply position the workpiece at the correct angle or alignment to allow the cutting tool to do its job accurately.
Both jigs and fixtures play a vital role in streamlining manufacturing, reducing human error, and improving production efficiency.
The Importance of Jigs and Fixtures in Manufacturing
The use of jigs and fixtures in manufacturing offers a wide range of benefits that make them indispensable tools in modern production processes. Some of the key advantages include:
-
Increased Productivity: Jigs and fixtures allow for faster setup times and minimize the need for adjustments between operations. Once a jig or fixture is set up for a particular workpiece, the process can proceed without constant reconfiguration.
-
Improved Accuracy and Precision: By ensuring the workpiece is held securely and in the correct position, jigs and fixtures help maintain accuracy in the machining process, reducing the likelihood of defects and improving the quality of finished parts.
-
Consistency and Repeatability: For mass production, consistency is critical. Jigs and fixtures ensure that each part is produced to the same specifications, making it possible to replicate parts with high precision.
-
Reduced Human Error: Jigs and fixtures automate the positioning of workpieces and tools, reducing the chances of errors caused by operator fatigue or misalignment. This leads to more reliable and high-quality products.
-
Enhanced Safety: Workpieces held firmly by jigs and fixtures are less likely to move unexpectedly during machining, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries caused by parts shifting or tools slipping.
Key Types of Jigs and Fixtures
Both jigs and fixtures come in various types, each designed for specific functions in manufacturing. Understanding these types will help determine which tools are best suited for particular tasks.
Types of Jigs
-
Drill Jigs Drill jigs are used to guide drill bits during drilling operations, ensuring that the holes are drilled at the correct location, size, and angle. They help to maintain the accuracy of hole placement across multiple workpieces.
Applications: Common in industries such as automotive and aerospace, drill jigs are often used to create holes in engine components, structural parts, and machine tools.
-
Milling Jigs Milling jigs are used in milling operations to guide cutting tools along precise paths. They help in cutting slots, grooves, or intricate shapes on a workpiece.
Applications: Milling jigs are widely used in the production of mechanical parts, gears, and aerospace components that require precise cuts and geometry.
-
Tapping Jigs Tapping jigs are designed to hold workpieces while guiding taps to create internal threads. They ensure that taps are aligned correctly during the threading process.
Applications: Tapping jigs are commonly used in the production of fasteners, threaded holes, and components requiring internal threads, such as in the automotive and machinery industries.
-
Boring Jigs Boring jigs are used to enlarge existing holes with precision. They guide boring tools to ensure that the hole's size and alignment meet specific tolerances.
Applications: Boring jigs are used in industries like automotive engine machining, aircraft manufacturing, and other precision metalworking operations.
Types of Fixtures
-
Vise Fixtures Vise fixtures are a type of clamping tool that holds workpieces in place during machining. They provide a stable and secure grip on the workpiece, allowing for various machining operations such as milling, drilling, and turning.
Applications: Vise fixtures are widely used in CNC machines, lathes, and milling centers, particularly in industries like aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and general metalworking.
-
Plate Fixtures Plate fixtures consist of a flat, rigid base onto which the workpiece is mounted. The plate can be equipped with clamping devices or locators to hold the workpiece securely during machining.
Applications: Plate fixtures are commonly used in industries requiring the machining of large components, such as the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
-
Locating Fixtures Locating fixtures are designed to position the workpiece accurately by using locators or pins that fit precisely into specific areas of the part. These fixtures ensure that parts are aligned properly for machining or assembly.
Applications: Locating fixtures are used in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where parts must be positioned with high accuracy to ensure a proper fit.
-
Assembly Fixtures Assembly fixtures hold multiple components together during the assembly process. They ensure that the components are aligned correctly and fit together as intended.
Applications: Used extensively in the automotive and electronics industries, assembly fixtures assist in the assembly of complex products such as vehicles, electronic devices, and machinery.
-
Welding Fixtures Welding fixtures hold parts in place during the welding process, preventing movement or misalignment while ensuring that the parts are welded with precision.
Applications: Welding fixtures are used in industries such as automotive, shipbuilding, and heavy equipment manufacturing, where strong and precise welded joints are critical.
Benefits of Using Jigs and Fixtures
The use of jigs and fixtures in manufacturing brings significant advantages:
1. Faster Setup Times
Jigs and fixtures streamline the setup process, reducing the time needed to position and secure workpieces. Once the tool is set up, it can hold parts securely and position them accurately for subsequent operations, improving efficiency.
2. High Precision
Jigs and fixtures provide repeatable and accurate placement of workpieces, ensuring that each part is produced to the required specifications. This precision is vital for industries that demand tight tolerances, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
3. Cost Savings
By reducing the need for manual adjustments, minimizing errors, and speeding up production times, jigs and fixtures contribute to lowering overall production costs. Manufacturers can produce more parts in less time and with fewer defects, resulting in significant savings.
4. Consistent Quality
With jigs and fixtures in place, manufacturers can produce parts with consistent dimensions and characteristics. This is crucial in high-volume manufacturing, where uniformity is essential for product functionality and assembly.
5. Improved Safety
By securely holding parts in place, jigs and fixtures prevent accidents caused by parts shifting unexpectedly during machining. This enhances worker safety and minimizes the likelihood of damage to machines or tools.
Applications Across Industries
Jigs and fixtures are used in numerous industries where precision and efficiency are paramount. Common industries and their applications include:
- Automotive: Jigs and fixtures are used to produce engine parts, body components, and assemblies with high precision, ensuring quality and repeatability in mass production.
- Aerospace: In aerospace manufacturing, jigs and fixtures are essential for the production of complex and highly accurate parts like wings, fuselages, and engine components.
- Electronics: For the assembly and testing of components like circuit boards, jigs and fixtures provide stability and precision, ensuring consistent performance.
- Medical Devices: Jigs and fixtures are crucial in the production of medical equipment, where accuracy and safety are vital for patient health.
- Heavy Machinery: Fixtures help hold large and heavy parts in place during machining operations, ensuring precise results and strong structural integrity.
Conclusion
Jigs and fixtures are vital tools in the world of manufacturing, enabling precision, repeatability, and efficiency across various production processes. By holding parts securely and guiding tools, they ensure that components are manufactured to the highest standards. Whether in automotive, aerospace, electronics, or other industries, the role of jigs and fixtures cannot be overstated. As manufacturing technology continues to evolve, these tools remain central to achieving higher levels of productivity and quality in production.