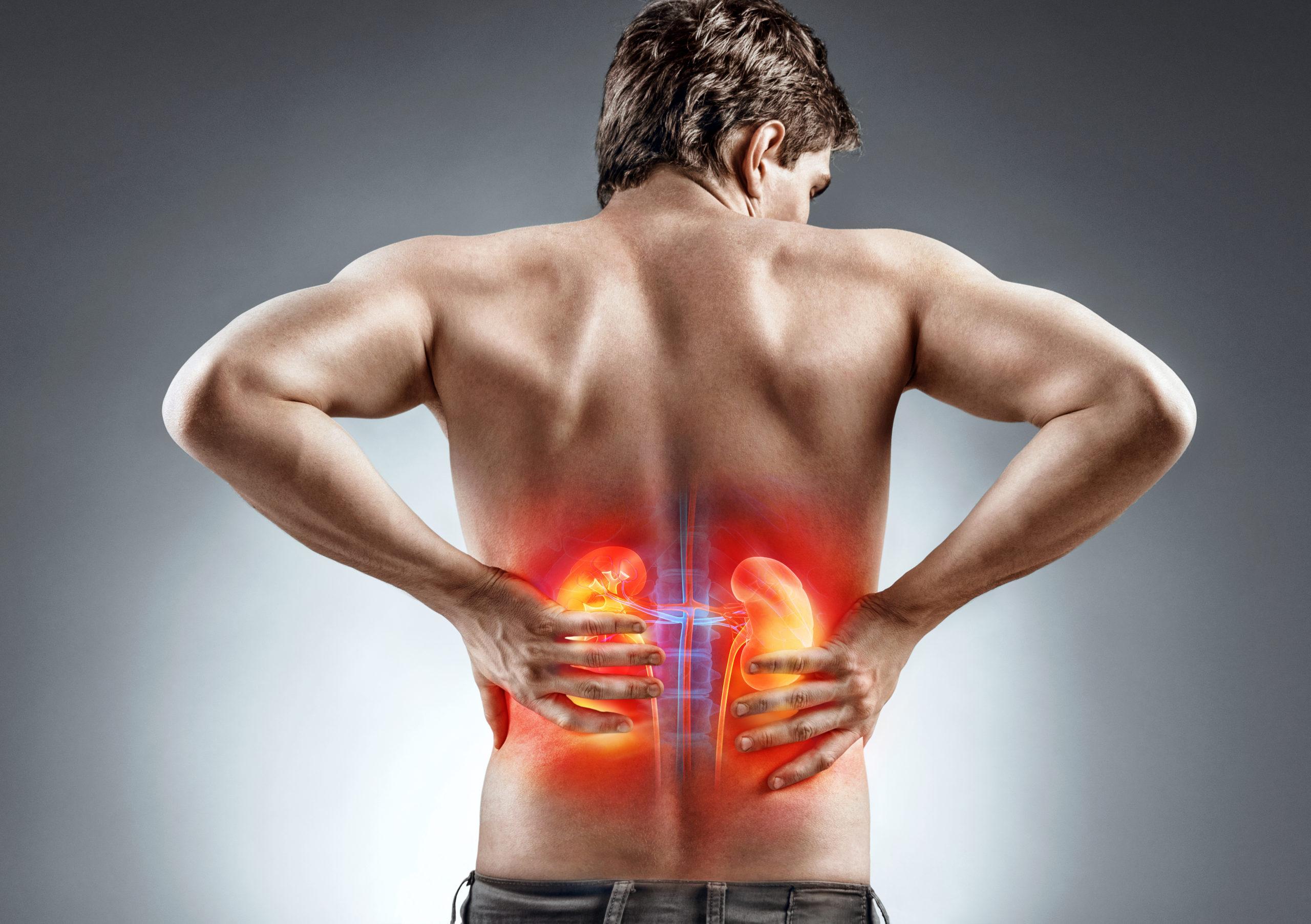
Kidney pain is a common yet concerning health issue that can point to various underlying conditions. Whether it’s a dull ache or a sharp stabbing sensation, kidney pain should never be ignored. This guide will help you understand what kidney pain is, its common causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and effective treatment options. If you’re experiencing discomfort, it’s essential to know when to seek medical advice—particularly from a nephrologist in Jaipur or your local area.
What Is Kidney Pain?
Kidney pain refers to discomfort originating from the kidneys—two bean-shaped organs located on either side of your spine, just below the rib cage. Pain may be felt on one or both sides and is typically located in the back, flank, or upper abdomen. Unlike muscular back pain, kidney pain is often deeper and may radiate to the groin or lower abdomen.
Common Causes of Kidney Pain
Kidney pain can arise from a variety of conditions, some acute and others chronic. Here are the most frequent causes:
1. Kidney Stones
These hard deposits of minerals and salts can block the urinary tract, causing intense, cramping pain that comes in waves.
Symptoms of kidney stones include:
-
Severe flank pain
-
Blood in urine
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Painful or frequent urination
2. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
When bacteria infect the urinary system—especially the kidneys (pyelonephritis)—it can result in back or side pain.
Symptoms of kidney infections:
-
Fever and chills
-
Painful urination
-
Foul-smelling or cloudy urine
-
Back or side discomfort
3. Polycystic Kidney Disease
This inherited condition causes cysts in the kidneys, which can lead to pain and eventual kidney failure if untreated.
Signs include:
-
Persistent dull back pain
-
High blood pressure
-
Recurring kidney infections
-
Blood in the urine
4. Kidney Injury or Trauma
Blunt force or impact to the lower back can cause kidney damage, leading to pain, bruising, or even internal bleeding.
5. Kidney Infection or Inflammation
Conditions like glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis cause inflammation, resulting in pain, fever, and swelling.
6. Kidney Cancer
Though rare, kidney tumors can cause flank pain, blood in urine, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
Symptoms Associated with Kidney Pain
Additional symptoms can help identify kidney-related issues:
-
Pain that worsens with movement or urination
-
Changes in urine color or smell
-
Frequent urination
-
Fever and chills
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Swelling (legs, ankles, around the eyes)
-
Fatigue
Kidney Pain vs. Back Pain
| Feature | Kidney Pain | Back Pain |
| Location | Flank or under ribs | Lower back or spine |
| Type of Pain | Dull ache or sharp, stabbing | Stiffness, soreness, muscle spasms |
| Radiation | Groin, lower abdomen | Legs or buttocks |
| Accompanying Symptoms | Fever, nausea, urinary changes | Limited movement, no systemic signs |
Understanding these distinctions can help you decide whether to consult a general practitioner or a nephrologist in Jaipur.
Diagnosing Kidney Pain
Your healthcare provider may use several tools to diagnose kidney pain:
-
Medical History & Physical Exam
-
Urine Tests – Detect infections, blood, or protein
-
Blood Tests – Check kidney function
-
Imaging (Ultrasound, CT Scan, MRI) – Identify stones, tumors, or abnormalities
Treatment Options for Kidney Pain
Treatment depends on the root cause:
1. Kidney Stones
-
Hydration: Helps flush out small stones
-
Pain relief: NSAIDs like ibuprofen
-
Medications: Alpha-blockers may assist in stone passage
-
Procedures: Lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or surgical removal for larger stones
2. Kidney Infections
-
Antibiotics
-
Pain relievers
-
Hospitalization for severe cases
3. Polycystic Kidney Disease
-
Blood pressure management
-
Pain control
-
Low-sodium diet
-
Regular kidney function monitoring
4. Kidney Injuries
-
Mild cases may resolve with rest and medication
-
Severe trauma might require surgical intervention
5. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
-
Managing blood pressure and diabetes
-
Dietary changes
-
Avoiding nephrotoxic medications
-
Dialysis or kidney transplant in advanced stages
Preventing Kidney Pain
While not all kidney issues are preventable, the following tips can help:
-
Stay hydrated
-
Maintain proper hygiene
-
Limit salt and processed foods
-
Avoid excessive use of NSAIDs
-
Control blood sugar and pressure
For those with ongoing issues or risk factors, regular check-ups with a nephrologist in Jaipur can be life-saving.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate care if you experience:
-
Severe or persistent kidney pain
-
Blood in urine
-
High fever
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Difficulty or painful urination
-
Body swelling
Conclusion
Kidney pain can be a warning sign of various serious conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to protect your kidney health. If you're uncertain about your symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional—or consult a trusted nephrologist in Jaipur for specialized care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Kidney Pain
1. What does kidney pain feel like?
A dull ache or sharp, stabbing pain in the side, back, or upper abdomen, sometimes radiating to the groin.
2. How do I know if it’s kidney pain or back pain?
Kidney pain is deeper, often constant, and usually includes other symptoms like fever or urinary changes.
3. Can kidney pain go away on its own?
Minor infections or small stones may resolve with fluids and rest, but persistent pain needs medical attention.
4. What are early signs of kidney problems?
Back pain, fatigue, swelling, changes in urination, high blood pressure, and nausea.
5. When should I see a doctor for kidney pain?
Immediately—if you have severe pain, fever, blood in urine, or vomiting.
6. Can dehydration cause kidney pain?
Yes. It concentrates urine and can lead to stones or infections.
7. What foods help with kidney pain?
Hydrating fluids, low-sodium meals, and foods low in oxalates like bananas and white rice.
8. Can stress cause kidney pain?
Not directly, but it can worsen underlying conditions affecting the kidneys.
9. How is kidney pain treated at home?
Mild pain may improve with hydration, a heating pad, and doctor-approved pain relievers.
10. Is kidney pain a sign of kidney failure?
Not always, but it can be. Other symptoms like fatigue, swelling, and reduced urination are more common in kidney failure.